Independent evaluations & analysis
Top line returns
🟢 Saving: √ Transportation costs. √ Storage costs. √ Fertilizer costs. √ Water costs. √ Land need / spreading. √ Discharge/gate fees. √ ++
🟢 Opportunities: √ New revenue streams. √ Nutrient Value. √ Manure Value. √ Bio-fertilizer products. √ AD feedstock/energy √ Carbon offset. √ ++
🟢 Environmental: √ GHG Emissions. √ Air Quality. √ Nutrient leaching. √ Eutrophication risk. √ Runoff risk. √ Soil Health. √ ++
🟢 Regulation: √ Regulation compliance. √ Environmental compliance. √ Improved local environment. √ Circular Agriculture. √ Scope 1 / 2 / 3 demands. √ Best Available Techniques’ √ ++
🟢 Operational: √ Efficient manure management. √ Water security. √ Targeted nutrient application. √ Animal welfare / pathogen spread. √ Highly automated / 365 monitoring. √ ++
How do we know?
To ensure our technology, systems and data are current:
► Run frequent independent analysis of our client’s input/output parameters.
► Submit output samples for EU bio-fertiliser PFC classification.
► Monitor EU Directive, Regulation, Pathways, Best Practice etc.
► Ongoing veterinary pathogen risk analysis updates.
► Access independently commissioned system evaluations and cost analysis.
► Co-ordinate with specialist engineering suppliers e.g. AD plants, separators…
3rd-party sources include: Eurecat, Aigüas Manresa, Fitchner, Labin among others.
{remove} {recover}
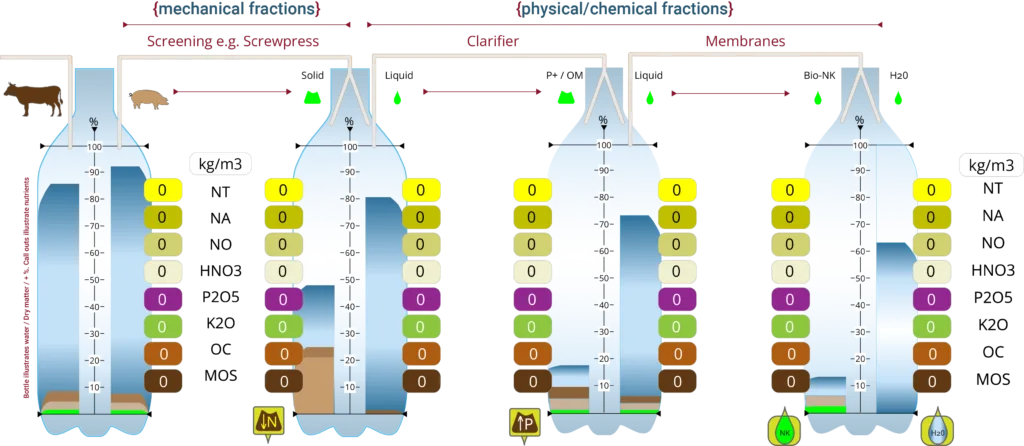
De-watering / Screening
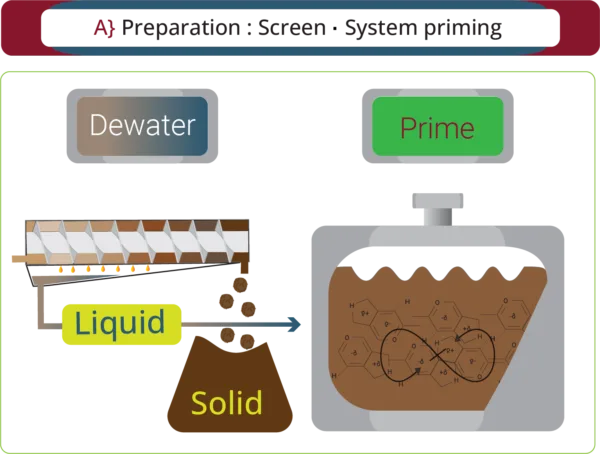
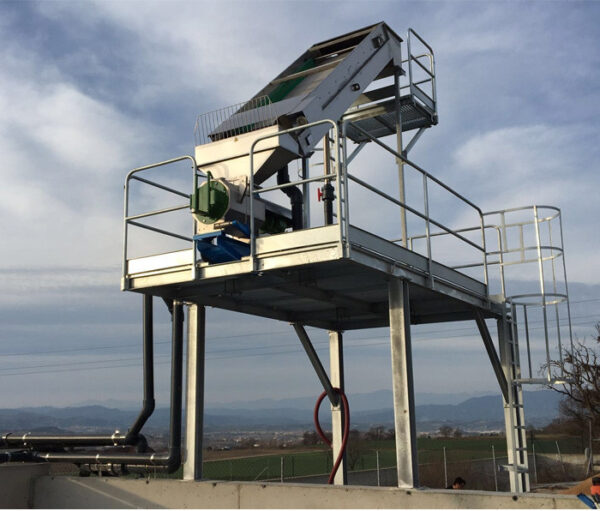
Pig Slurry – due to the high water content, a combined ramp/screw-press system is an energy efficient method e.g. Segalés Kompack range (pictured).
Cow Slurry – with higher DM content, screw separators are effective for use with green bedding systems or composting.
Digestates – given their honey/treacle consistency, a decanting centrifuge can improve the reactors efficiency.

Physical / Chemical Reactor
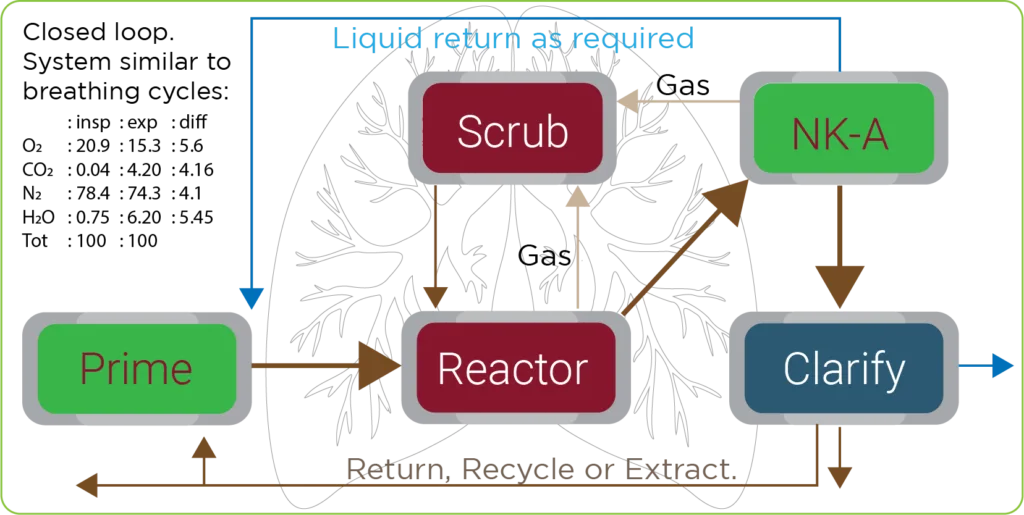
The easiest way to imagine our system is similar to breathing in and out – the intake of new while prior is processed before being expelled.
| Humans | nkaptur | ||||
| In | Out | In | Out | ||
| O2 | 20.9 | 15.3 | Dissolved | N,K Liquid | |
| CO2 | 0.04 | 4.20 | Suspended | N,P Solids | |
| N2 | 78.4 | 74.3 | OM | + OM | |
| H2O | 0.75 | 6.20 | H2O | H2O | |
| Tot | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
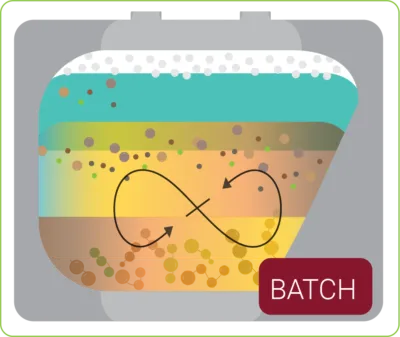
Batch reactor
Suited for producers with low volume variations or ‘cluster’ sites for multiple farms using scheduled tanker deliveries.
► System is set up process a fixed volume per session.
► Single bay with timed compound addition.
► Apatite/solid extracted from reactor.
► Buffer tanks regulate processing.
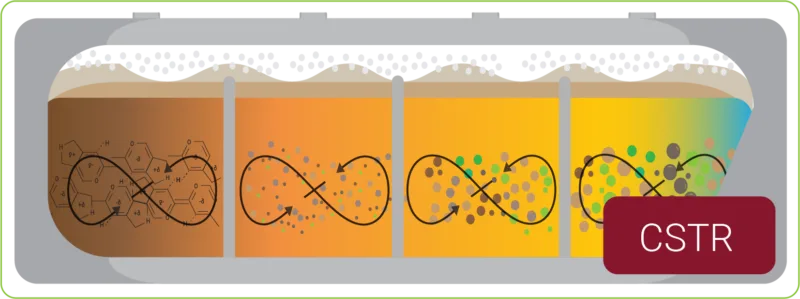
Continuous Cascade Reactor – New for 2025
The CST Reactor is our newest system innovation, developed to allow automated ‘pit to processed’ with low power requirements, efficient compound addition, reduced human intervention and volume variation through the year.
► System runs as a variable continuous flow.
► Improved coagulant performance in reactor.
► Apatite / solid removal after flocculation.
Membrane Technologies
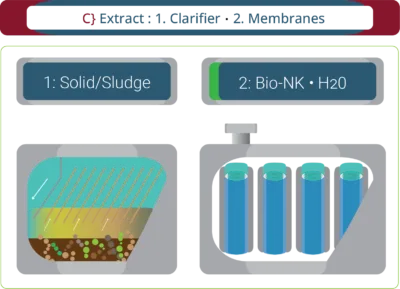
Variable: dependent on client need / goals.
While some clients may wish to retain the untreated liquid for direct application, the final process is tailored to client’s needs.
► Water volume, reuse and purity requirements.
► Bio-NK for application needs or conversion into PFC classified bio-fertilizer.
{reuse} {refine}
Solid Fraction (DM↓N) + Liquid Fraction – A (LF-A) via Mechanical Screening

LF-A (±80%)
Suspended fine solids, ammonium nitrogen, potassium, some dissolved phosphorus. Original water content of ±87%.
=> Physical/Chemical stage.
DM↓N (±20%)
Phosphorus (bound to organic matter), organic nitrogen, fibrous solids, trace minerals.
At this point, with dry matter ±40%, the material is beyond standard classifications for ‘solid manure’ of 15-25% DM):
{reuse}
► Green bedding systems
► Anaerobic digester feedstock (reduced ammonium nitrogen content).
► Direct application for soil enrichment.
{refine}
► Composting
DM↑P + Liquid Fraction-B (LF-B) via Physical / Chemical / Clarifying.

LF-B
Predominately H20, rich in dissolved N (ammonium), P & K.
=> Membrane stage.
Solid (Sludge) DM↑P
Remaining phosphorus, residual solids and organic N, trace minerals
{reuse}
► Combine and use with DM↓N.
► Combine with permeate / Bio-NK for summer application, where P required.
{refine}
►Composting.
►Commercial bio-fertilizer ingredient.
Bio-NK & Permeate H2O via Membrane technologies

Bio-NK
New 2025: A PFC organic fertilizer base source.
Concentrate
► High-N,
► High-K
► pH 6-7
{reuse}
► Fertigation,
► Direct application; growing season.
► Sale.
{refine} NEW 2025
►Concentrate for commercial PFC bio-fertiliser ingredient.
Permeate H20
ZERO DM, ZERO P, ZERO K,
► Trace HNO3 @ <50ppm,
► Conductivity @<0.5µS/cm,
► pH 6-7.
{reuse}
► Compliant discharge including recharging wells / watercourses.
►Farm use including washing, flushing, cooling, irrigation…
{refine}
► Connect to ‘clean water’ systems for livestock.
► Additional purification for consumption, polish….
Independent analysis – pig slurry – Feb 2025
Raw
Kg/m3
| N (Kjeldhal) | 6.25 |
| N (amoniacal) | 3.54 |
| N (orgànic) | 2.71 |
| N (nitric) | 2 |
| P2O5 | 1.68 |
| K2O | 3.67 |
Combined solids
Kg/m3
| N (Kjeldhal) | 5.25 |
| N (amoniacal) | 3.22 |
| N (orgànic) | 2.03 |
| N (nitric) | 1.20 |
| P2O5 | 1.68 |
| K2O | 3.08 |
Bio-NK Liquid
Kg/m3
| N (Kjeldhal) | 3.98 |
| N (amoniacal) | 1.27 |
| N (orgànic) | 2.71 |
| N (nitric) | 3.20 |
| P2O5 | 0.00 |
| K2O | 2.35 |
Concentrate-nk @80%
Kg/m3
| N (Kjeldhal) | 19.92 |
| N (amoniacal) | 6.37 |
| N (orgànic) | 13.55 |
| N (nitric) | 16.00 |
| P2O5 | 0.00 |
| K2O | 11.74 |
Regulations

EU Directives Affecting Agriculture • European Green Deal (climate-neutral by 2050)
Rock / Hard place.
Quality sustainable and affordable food + increased legislation + instability + rising costs…. but briefly:
Current regulations + Future goals = Complexity.
We can’t follow every local bylaw change but we aim to be as up-to-date as possible across regulation amendments.
On your farm today.
✅ Cleaner water
✅ Biodiversity protection
✅ Reduced pollution
✅ Sustainable soil and land use
✅ Climate-smart agriculture
Coming soon to a farm near you.
✅ Achieve climate neutrality by 2050 (zero net emissions).
✅ Reduce pollution, water use, and biodiversity loss.
✅ Transition to a circular economy (reduce waste, reuse resources).
✅ Promote sustainable food systems under the Farm to Fork Strategy.
✅ Improve rural development and resilience to climate change.
Ongoing R&D
Pathogen reduction.
After a recent veterinary process review and discussions on viral contagion e.g. prrs onto different sites, especially after direct slurry application though airborne dispersal, we are looking at how to expand our testing parameters to include livestock virus reductions.
Current testing: Salmonella and E-coli for EU Reuse of Water in Agriculture (2020/741), Drinking Water Directive 2020/2184…
Results for Salmonella and E-coli
► Raw: Salmonella – Detected / E-coli: 9,00E+03 NMP/g
► De-watered solids*: Salmonella – detected / E-coli: 1,50E+04 NMP/g
► Post Reactor Bio-NK & H2O: Salmonella – not detected / E-coli – 3,00E+02 NMP/g
*Pathogens can be removed through correct composting procedure, especially using reactors, where temperature control is vital.
‘Zero’ {on-site slurry}?
‘zero’-slurry may not be possible (biologically) with live animals on site, but as ‘near-zero’ as possible: solids used for AD or composting reactors, Bio-NK liquid sent for bio-fertilser production and water discharged or reused, could it be possible to have ‘near-zero’ on-site slurry?
‘Zero’ {land/disposal requirements}?
For farms where land disposal is a problem, with >60% of the original content permeate water, the opportunity to repurpose solids and Bio-NK storage a fraction of the original volume and suitable for PFCs – what turns slurry from a liability to an opportunity?